New Altair SimSolid hydrostatic pressure load
Hydrostatic pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity. Hydrostatic pressure increases in proportion to depth measured from the surface because of the increasing weight of fluid exerting downward force from above.
Typical examples of hydrostatic pressure include a large body of water exerting force on a dam or the force creating by fluids within a pressurized tank.
Now available in the latest release of Altair SimSolid Power edition, hydrostatic loads can be easily defined using the following methodology. First open the new Hydrostatic loads dialog found in the structures workbench.
Next, select the faces on the model where the pressure will be applied. Then, locate the fluid surface by defining a XYZ point on the surface and a vector that indicates the depth (gravity) direction. Note that while this can be entered on the dialog, it is often easier to just drag the water surface indicator (the sphere at the center of the concentric circles) to the desired location.
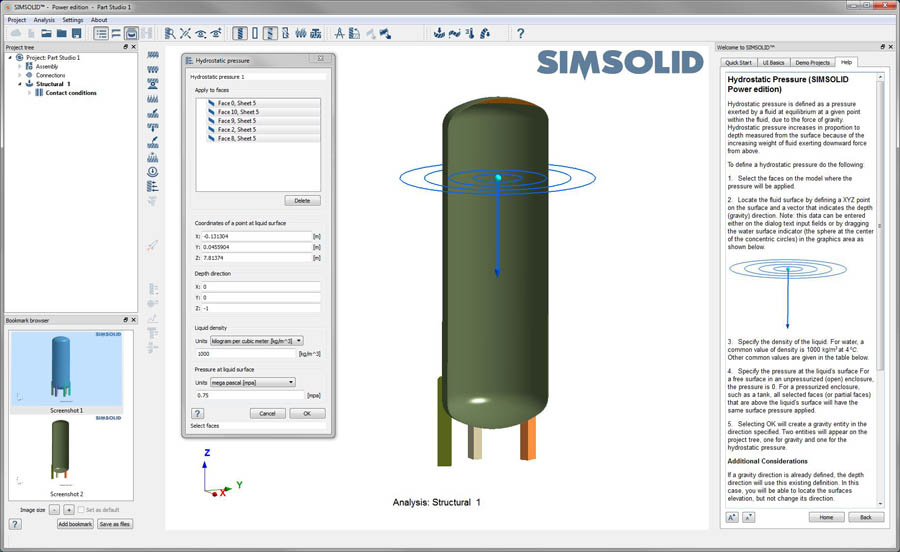
Next, specify the density of the liquid and the pressure at the liquid’s surface. For a free surface in an unpressurized (open) enclosure, the pressure is 0, but for a pressurized enclosure, such as a tank shown here, a uniform pressure will exist on and above the liquid’s surface. It is assumed that all selected faces (or partial faces) above the liquid’s surface will have the same pressure as is applied to the surface. This make it easy to pressurize a container.
Finally, selecting OK will automatically create a gravity entity in the direction specified. Two entities will appear on the project tree, one for gravity and one for the hydrostatic pressure.
That’s all there is to it.
Typical examples of hydrostatic pressure include a large body of water exerting force on a dam or the force creating by fluids within a pressurized tank.
Now available in the latest release of Altair SimSolid Power edition, hydrostatic loads can be easily defined using the following methodology. First open the new Hydrostatic loads dialog found in the structures workbench.

Next, select the faces on the model where the pressure will be applied. Then, locate the fluid surface by defining a XYZ point on the surface and a vector that indicates the depth (gravity) direction. Note that while this can be entered on the dialog, it is often easier to just drag the water surface indicator (the sphere at the center of the concentric circles) to the desired location.

Next, specify the density of the liquid and the pressure at the liquid’s surface. For a free surface in an unpressurized (open) enclosure, the pressure is 0, but for a pressurized enclosure, such as a tank shown here, a uniform pressure will exist on and above the liquid’s surface. It is assumed that all selected faces (or partial faces) above the liquid’s surface will have the same pressure as is applied to the surface. This make it easy to pressurize a container.
Finally, selecting OK will automatically create a gravity entity in the direction specified. Two entities will appear on the project tree, one for gravity and one for the hydrostatic pressure.
That’s all there is to it.




