Data Analytics Delivers Competitive Edge, On and Off the Track
Advancements in data analytics technology have made collecting massive amounts of data and extracting insights from this data easier and more valuable than ever before. Now, with the right tools, almost anyone can retrieve, analyze, and use smart data to make more informed decisions for whatever their needs may be.
Having access to the right data at the right time can mean major cost savings, greater operational efficiency, and the ability to predict and resolve issues before they even occur.
In an industry where a fraction of a second can mean the difference between winning and losing, racing teams have found ways to utilize data analytics, including telemetry, to gain competitive advantages and better understand drivers and their vehicles to improve lap times.
The Transformation of Telemetry and Data Transmission
Telemetry systems are a type of specialized technology that are used to measure and transmit data from a source to equipment for monitoring. This data can come from a variety of sources and is typically transmitted from a remote location with sensors using a wireless form of communication, such as radio or cellular signal.
Telemetry has been used since the 19th century, when data transmission was only feasible through a wired connection. In the U.S., one of the first common uses of wired telemetry systems was within the industrial sector to record and monitor electricity distribution throughout households in Chicago, Illinois. With advances in wireless and cloud technology, data transmission has evolved to accommodate massive data collection and transmission from wireless systems of connected devices all over the world.
This technology now has applications in a multitude of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, marine, healthcare, automotive, and more. Within manufacturing, telemetry systems can assist in transmitting real-time data for the monitoring of equipment failure and even predictive maintenance for machinery. In agriculture, farmers can use sensors linked to their crops to measure soil moisture and ensure their entire farm is maintained. No matter the industry, taking advantage of analyzing operational data can bring an organization valuable insights.
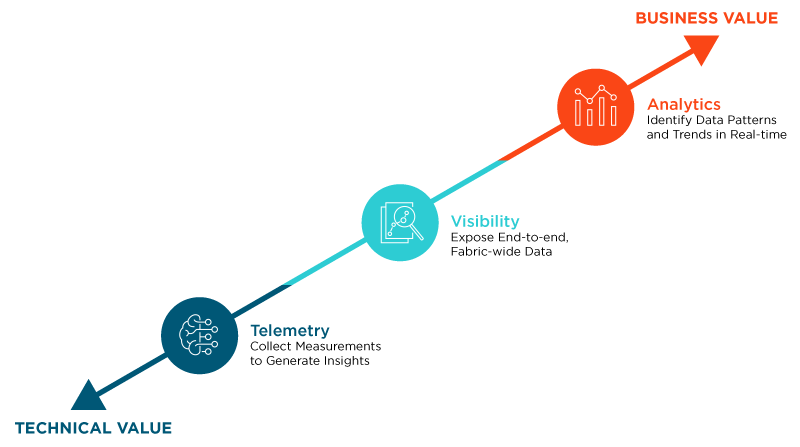
Within the racing industry, Formula One racing has been benefitting from data analytics to optimize race car design and performance.
Telemetry in Formula One Racing
Since the 1980s, Formula One racing has been using telemetry with race cars to understand and improve vehicle performance. Drivers and engineers alike benefit from this technology because, with these insights, drivers can find ways to perfect their own driving, and on the back end, engineers can use this data combined with simulation tools to improve the design of the race cars. With the aid of telemetry, real-time visualization of data during a race can play a key role in a driver’s next win on the track.
Considering the complexity of a race car, engineers especially need to consider the effects that changes to the car’s design and tuning will have on the performance and safety of the vehicle. Telemetry data provides these simulation tools with more accurate inputs to assess how modifications will affect structural loads, aerodynamics, acceleration and handling, and fuel efficiency.
During trial exercises and races, race cars are equipped with hundreds of sensors that send data to race teams through radio signal, as well as sensors typically placed around a track. Data such as speed, steering angles, fuel consumption, directional forces, suspension data such as damper movements and loads, and more are monitored live by the pit crew. In 1991, the first F1 team to apply telemetry was McLaren, and when the technology was first introduced, teams could only record small bursts of data each time the driver passed the crew. Now, thanks to technological advancements, data can be received at any point on the track.
Racing with Real-time Data Analytics
Using Altair Panopticon™, Altair simulated Formula One vehicles driving on the Austria-Spielberg racecourse to demonstrate its instant data processing capabilities. Panopticon is a real-time visualization engine capable of consuming, transforming, and displaying data. With a drag and drop interface, Panopticon allows users to fully interact with data, manipulate it, and view customized graphs depending on which information they would like to see.
Watch the full video demonstration here.
During the race simulation, data such as speed, brake temperature, and driver inputs were instantly visible during each lap the vehicle made. Similar to live races, Altair was able to monitor for anomalies and set alerts if certain data goes outside of a set range. For instance, if tire pressure drops below a desired threshold, teams can immediately react by scheduling a pit stop and inform the driver to adjust their behavior to maximize performance under these new conditions.
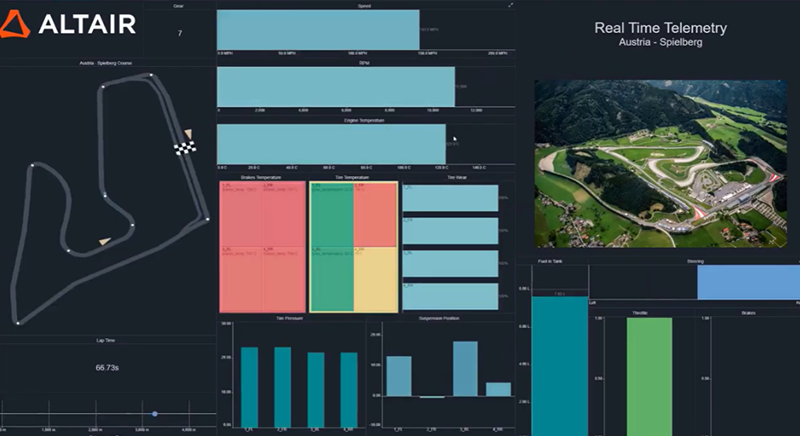
With a customizable dashboard, users can observe individual drivers and laps, how they performed on corners, and plot this information onto a graph for convenient visuals. Below is an example showing how benchmark data can be compared against data from other laps, other drivers, or other races during the simulation. In this graph, the data shows that on one corner, the benchmark lap had a higher average speed, applied the throttle longer, and applied the brake more smoothly than the chosen lap, leading to a faster overall split time during the race.
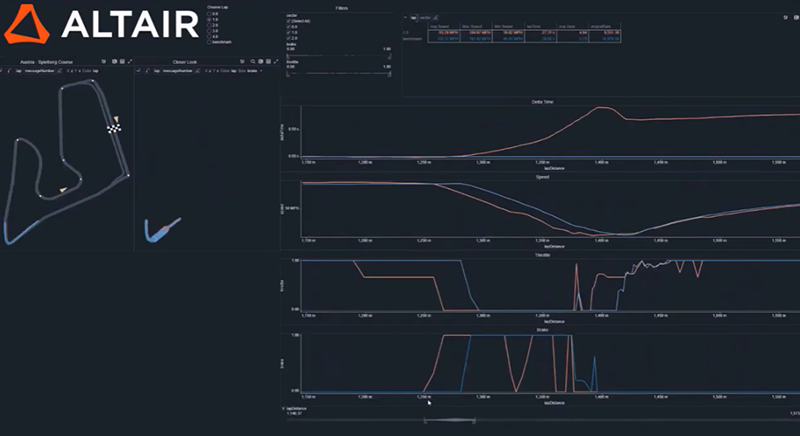
Panopticon enables track-side analysts to view multiple real-time streams simultaneously and make on-the-fly comparisons with historical data. This enables them to observe how a run is evolving over time, identify trends during a race, and anticipate how a car will perform in the future.
Data Analytics and Simulation
On-track measured racing data can be combined with physics simulation to give racing engineers additional insights into improving vehicle performance. With real-world feedback from telemetry data feeding a digital twin, designers can virtually test design modifications quickly and accurately assess their potential impact on the track.
One tool that is bridging the gap between simulation and quantitative data is ChassisSim. ChassisSim is a race car simulation tool that provides users with dynamic data; meaning the vehicle’s performance can be simulated in real time as if the car is racing live on a track. ChassisSim is available to Altair users through the Altair Partner Alliance.
With driver-in-the-loop capabilities, realistic driver actions and feedback can be coupled with lap time simulation to predict accurate lap times, allowing for data to be exported and reviewed. In a recent application of ChassisSim by the Institute of Mechanical Engineers UK, where a virtual dynamics competition was held, the student group utilized the software to simulate acceleration, skid-pad, and sprint events during the competition.
Leveraging data analytics and telemetry in racing provides more than just a smoother ride for the driver. Using that data provides every team member with more insight on how to improve future lap times for the next race. Pairing data with simulation tools gives drivers and racing teams access to all the information they need to maximize performance.
Find out how Altair’s technology is leveraged by racing manufacturers like Ducati, Dallara, and Griiip to gain a winning edge. Click here to learn more about Altair's data analytics solutions.
Having access to the right data at the right time can mean major cost savings, greater operational efficiency, and the ability to predict and resolve issues before they even occur.
In an industry where a fraction of a second can mean the difference between winning and losing, racing teams have found ways to utilize data analytics, including telemetry, to gain competitive advantages and better understand drivers and their vehicles to improve lap times.
The Transformation of Telemetry and Data Transmission
Telemetry systems are a type of specialized technology that are used to measure and transmit data from a source to equipment for monitoring. This data can come from a variety of sources and is typically transmitted from a remote location with sensors using a wireless form of communication, such as radio or cellular signal.
Telemetry has been used since the 19th century, when data transmission was only feasible through a wired connection. In the U.S., one of the first common uses of wired telemetry systems was within the industrial sector to record and monitor electricity distribution throughout households in Chicago, Illinois. With advances in wireless and cloud technology, data transmission has evolved to accommodate massive data collection and transmission from wireless systems of connected devices all over the world.
This technology now has applications in a multitude of industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, marine, healthcare, automotive, and more. Within manufacturing, telemetry systems can assist in transmitting real-time data for the monitoring of equipment failure and even predictive maintenance for machinery. In agriculture, farmers can use sensors linked to their crops to measure soil moisture and ensure their entire farm is maintained. No matter the industry, taking advantage of analyzing operational data can bring an organization valuable insights.
Within the racing industry, Formula One racing has been benefitting from data analytics to optimize race car design and performance.
Telemetry in Formula One Racing
Since the 1980s, Formula One racing has been using telemetry with race cars to understand and improve vehicle performance. Drivers and engineers alike benefit from this technology because, with these insights, drivers can find ways to perfect their own driving, and on the back end, engineers can use this data combined with simulation tools to improve the design of the race cars. With the aid of telemetry, real-time visualization of data during a race can play a key role in a driver’s next win on the track.
Considering the complexity of a race car, engineers especially need to consider the effects that changes to the car’s design and tuning will have on the performance and safety of the vehicle. Telemetry data provides these simulation tools with more accurate inputs to assess how modifications will affect structural loads, aerodynamics, acceleration and handling, and fuel efficiency.
During trial exercises and races, race cars are equipped with hundreds of sensors that send data to race teams through radio signal, as well as sensors typically placed around a track. Data such as speed, steering angles, fuel consumption, directional forces, suspension data such as damper movements and loads, and more are monitored live by the pit crew. In 1991, the first F1 team to apply telemetry was McLaren, and when the technology was first introduced, teams could only record small bursts of data each time the driver passed the crew. Now, thanks to technological advancements, data can be received at any point on the track.
Racing with Real-time Data Analytics
Using Altair Panopticon™, Altair simulated Formula One vehicles driving on the Austria-Spielberg racecourse to demonstrate its instant data processing capabilities. Panopticon is a real-time visualization engine capable of consuming, transforming, and displaying data. With a drag and drop interface, Panopticon allows users to fully interact with data, manipulate it, and view customized graphs depending on which information they would like to see.
Watch the full video demonstration here.
During the race simulation, data such as speed, brake temperature, and driver inputs were instantly visible during each lap the vehicle made. Similar to live races, Altair was able to monitor for anomalies and set alerts if certain data goes outside of a set range. For instance, if tire pressure drops below a desired threshold, teams can immediately react by scheduling a pit stop and inform the driver to adjust their behavior to maximize performance under these new conditions.
With a customizable dashboard, users can observe individual drivers and laps, how they performed on corners, and plot this information onto a graph for convenient visuals. Below is an example showing how benchmark data can be compared against data from other laps, other drivers, or other races during the simulation. In this graph, the data shows that on one corner, the benchmark lap had a higher average speed, applied the throttle longer, and applied the brake more smoothly than the chosen lap, leading to a faster overall split time during the race.
Panopticon enables track-side analysts to view multiple real-time streams simultaneously and make on-the-fly comparisons with historical data. This enables them to observe how a run is evolving over time, identify trends during a race, and anticipate how a car will perform in the future.
Data Analytics and Simulation
On-track measured racing data can be combined with physics simulation to give racing engineers additional insights into improving vehicle performance. With real-world feedback from telemetry data feeding a digital twin, designers can virtually test design modifications quickly and accurately assess their potential impact on the track.
One tool that is bridging the gap between simulation and quantitative data is ChassisSim. ChassisSim is a race car simulation tool that provides users with dynamic data; meaning the vehicle’s performance can be simulated in real time as if the car is racing live on a track. ChassisSim is available to Altair users through the Altair Partner Alliance.
With driver-in-the-loop capabilities, realistic driver actions and feedback can be coupled with lap time simulation to predict accurate lap times, allowing for data to be exported and reviewed. In a recent application of ChassisSim by the Institute of Mechanical Engineers UK, where a virtual dynamics competition was held, the student group utilized the software to simulate acceleration, skid-pad, and sprint events during the competition.
Leveraging data analytics and telemetry in racing provides more than just a smoother ride for the driver. Using that data provides every team member with more insight on how to improve future lap times for the next race. Pairing data with simulation tools gives drivers and racing teams access to all the information they need to maximize performance.
Find out how Altair’s technology is leveraged by racing manufacturers like Ducati, Dallara, and Griiip to gain a winning edge. Click here to learn more about Altair's data analytics solutions.




