Five Applications of Knowledge Graphs in the Drug Discovery Process
In the pharmaceutical industry, data drives every stage of the drug life cycle, from research and development (R&D) to post-market surveillance. But with data comes data silos. Data integration and access become hurdles that require experts to spend time tracking data down instead of focusing on their life-changing work. Enterprise data is complex and unwieldy, often locked in a variety of structured and unstructured sources. Knowledge graphs integrate structured and unstructured data sources (including PDFs, emails, and more) and improve executive decision-making, enable experts to focus on their research, and meet regulatory compliance.
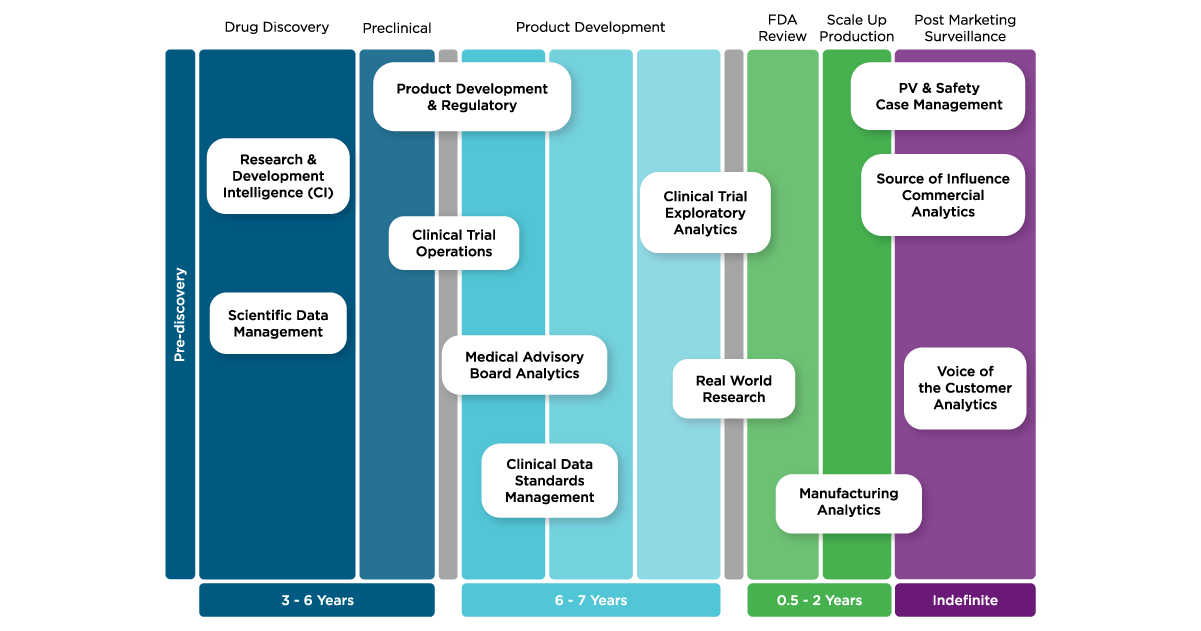
Here are five examples across the drug development process showcasing how knowledge graphs are transforming data for pharmaceutical companies to obtain business value and change lives.
1. Cancer research
Cancer affects many people’s lives, directly and indirectly. Every day, researchers are pioneering new and effective treatments, turning what were once life-ending diagnoses into treatable, manageable, and survivable illnesses with minimum long-term disruption to the patient’s life. Cancer research requires access to data from multiple sources, each with unique structures but little interconnection. Researchers must integrate this data to analyze it effectively. Enter knowledge graphs. They break down siloes and integrate data to create holistic, flexible, and scalable systems. Researchers are empowered to pursue their life-changing work without spending valuable time tracking down information from disparate data sources. By simplifying data access, they make quicker, fully informed decisions that accelerate their research.
2. Clinical Trial Operations
Clinical trials involve many data-intensive moving parts: site information, substance information, dosages, study protocols, adverse event reports, training records, and more. These are complex variables that must be managed effectively, efficiently, and at scale so scientists can monitor and maintain control over clinical trial operations without spending valuable time and money hunting information in siloed data sources. Knowledge graphs are the backbone to conversational analytics systems that turns data from structured and unstructured sources alike into an askable format by supporting the implantation of intuitive natural language user interfaces. With these systems in place, users without domain expertise can ask the system complex questions about the included clinical trials and receive detailed, complete, and accurate responses based on all the data available to the system.
3. Batch Genealogy
Once a new drug has successfully completed clinical trials and cleared regulatory requirements, it’s time to move into production, which brings a set of challenges. Every facet of a drug batch, from how it’s manufactured to where it’s used globally, is stored in individual files. Often, there is no interoperability between data siloes, and what systems do exist are lacking in scalability and sustainability. Knowledge graphs offer an integrated, scalable, and sustainable path forward to batch genealogy. Users can find new correlations and relationships in the data through knowledge graphs. Using this technology, pharmaceutical manufacturers can institute strict data traceability to understand everything about the batch: the manufacturing process (at what temperature was it made, stirring speed), transportation (cold chain versus standard), and how it’s stored. Such traceability enables manufacturers to visualize relationships between entities, maintain quality control, perform advanced yield analysis, support predictive maintenance, and perform root cause analysis for failures more efficiently.

4. Patient Safety
Pharmaceutical companies strive to change lives for the better. But without patient safety, their mission falls apart. Safety experts monitor patients in clinical trials; however, the relevant data exists in disparate ecosystems, with little connectivity between them. Knowledge graphs pull information from every available source, including clinical trials literature, patient files, medical histories, drug interaction databases, and more. Experts can then prioritize safety throughout clinical trials and beyond following production. Knowledge graphs support ad-hoc queries using natural language interfaces along with artificial intelligence (AI) workflows. With this advanced data integration, experts can identify risk factors, detect and analyze signals, and produce detailed reports at speed and scale
5. Identification of medicinal products
Maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Identification of Medicinal Products (IDMP) is a series of strict standards used globally to identify drugs in medicinal products. IDMP is mandatory in the EU by the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and under consideration by regulatory bodies in globally. For consumers, it means error-free, safer medicine. For pharmaceutical companies, it functions on a variety of levels. Firstly, IDMP adoption standardizes drug information across the entire supply chain. Each drug at each dosage for every product label requires precise IDMP information. Manufacturers can identify shortages of medication based on information pulled together by knowledge graphs at the earliest possible stage. In turn, they can notify authorities of incoming shortages months in advance. Secondly, IDMP tracks critical information on potentially dangerous chemicals to the environment and people, like polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Knowledge graphs can track PFAS and substances throughout the product management life cycle to easily pinpoint in which products they can be found.
6. Unify Your Data
There’s a common thread in each of these trends: a critical lack of data integration. Without knowledge graphs, analysts, experts, and researchers spend too much time pursuing valuable information locked in multiple siloed databases, data lakes, data warehouses, and documents. The chances of missing important connections or allowing errors to creep into analyses are high without effective data integration. In the past, integrating data using traditional systems required substantial investments of time and money, and the results were difficult to scale and adapt to incorporate new data sources or new types of queries. Knowledge graphs enable pharmaceutical developers to build flexible and scalable data systems compliant with modern enterprise architectures to access and analyze every available source of data efficiently and quickly. Business leaders can make better decisions based on new insights derived from richly connected data. In turn, researchers can pursue their real work: bettering lives and changing the world around us.
Contact us to learn how to leverage the power of knowledge graphs.




