Examining the Data on Digital Twin in the Automotive Industry
As the data in our Digital Twin Global Survey Report indicates, digital twin technology is already bringing together simulation, high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI), and data science in groundbreaking ways. In our latest research report, we turn our focus on digital twin technology in the automotive sector.
In this article, we’ll examine the data we gathered last year from an independent, international online survey of 2,007 professionals to see when, why, and how the automotive industry is adopting digital twin technology, what digital twin’s future is in the industry, and more.
Digital Twin Adoption and Usage in the Automotive Industry
In our survey, we examined questions relating to the adoption of digital twin technology within the automotive industry and how these companies are using the technology. To begin, we wanted to see what percentage of automotive organizations have already adopted digital twin, what technologies they’re using alongside it, how the automotive industry compares to its counterpart industries, and more.
The data shows that the automotive industry already uses digital twin technology widely, and that adoption has been relatively recent – many organizations started using it within the past year or sooner. At the same time, the data also suggests that the automotive industry is still trying to figure out how to fully utilize digital twin technology and determine where it fits in their design and manufacturing workflow. Let’s examine the data further.
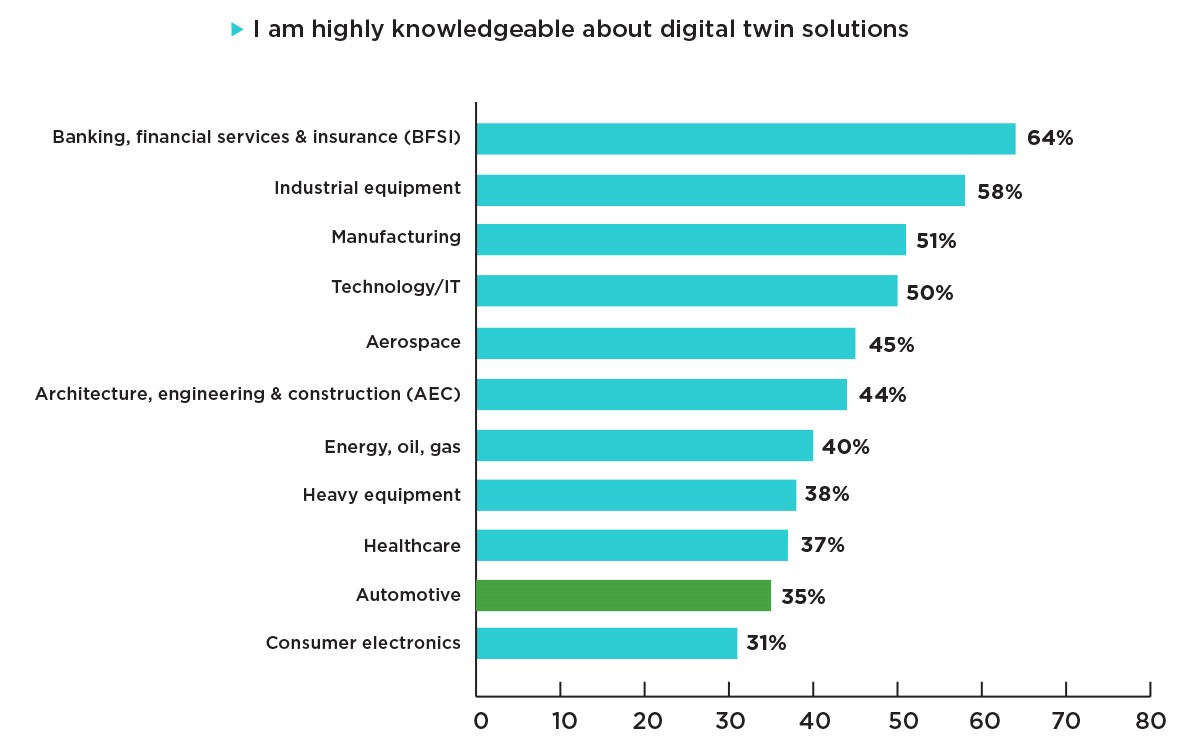
First off, of the automotive respondents within the overall survey, 76% said their organizations already leverage digital twin technology. For this question, only the heavy equipment industry had a higher proportion of affirmative responses (77%). The automotive sector’s response was seven points higher than the overall survey’s average (69%). That said, only 35% of automotive respondents said they are “highly knowledgeable about digital twin solutions” – the second-lowest percentage ahead of the consumer electronics industry (31%). Overall, this proportion of responses on “digital twin knowledgeable” was 15 points lower than the overall survey average.
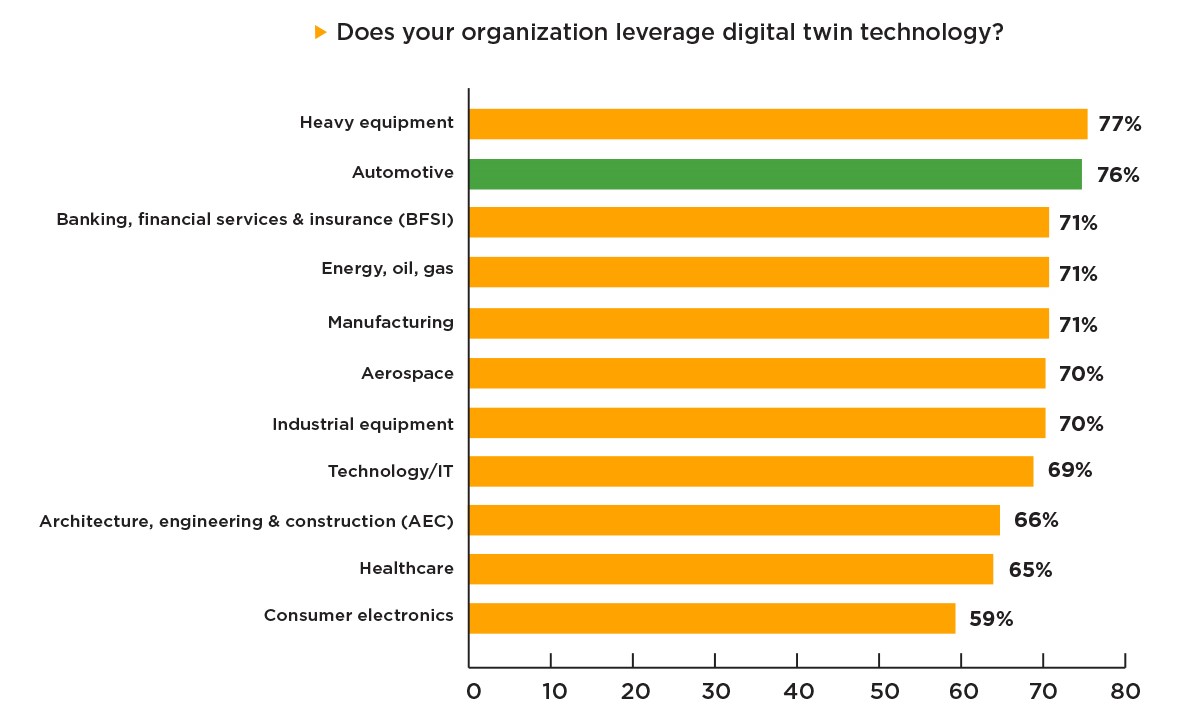
In addition, the data shows that automotive respondents seemed hesitant to call it a vital piece of their operations at the moment. Of respondents who said their organizations leverage digital twin technology, 97% said it was “important” to their organization – in line with the overall survey’s average. However, just 43% said it was “very important,” which was 20 points lower than the overall survey average (63%) and the second-lowest proportion out of all the industries surveyed.
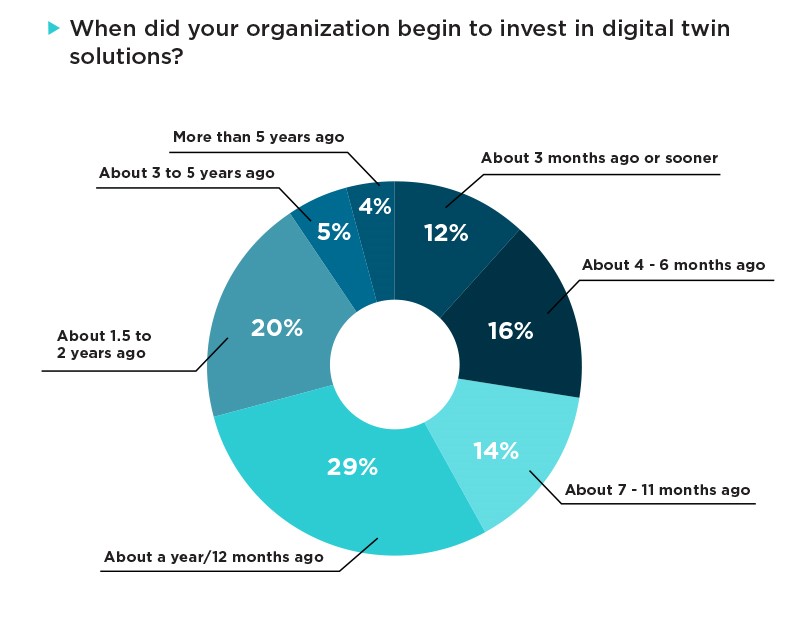
We also see that adoption times vary, but that adoption has mostly been recent. Of automotive respondents who said their organization already uses digital twin technology, 28% said their organization began investing in digital twins within the past six months or sooner; 29% said about a year ago, 20% said about one and a half to two years ago, and 9% said three or more years ago. The automotive industry was more likely than other industries in the survey to have adopted digital twins within the past six months by five points.
We find the most interesting insight here to be the paradox between adoption and understanding. Respondents from the automotive industry were more likely than almost every other industry to use digital twin technology – and simultaneously less likely than almost every other industry to say they’re highly knowledgeable about it.
It’s also worth noting that the automotive industry wasn’t very likely, compared to other industries, to say digital twin was “very important” to their organization. The responses to this question could reflect the automotive industry’s longstanding reliance on physical design, prototyping, and testing. As time goes on and as more organizations discover how the technology can reduce testing and hasten time to market, this is a statistic that could change drastically.
Digital Twin's Impact in the Automotive Industry
Here, we’ll examine what impact the technology is having on automotive organizations’ processes and products today. Most encouragingly, the data revealed the technology’s remarkable impact on sustainability – something that could multiply as organizations learn to use the technology in better ways.
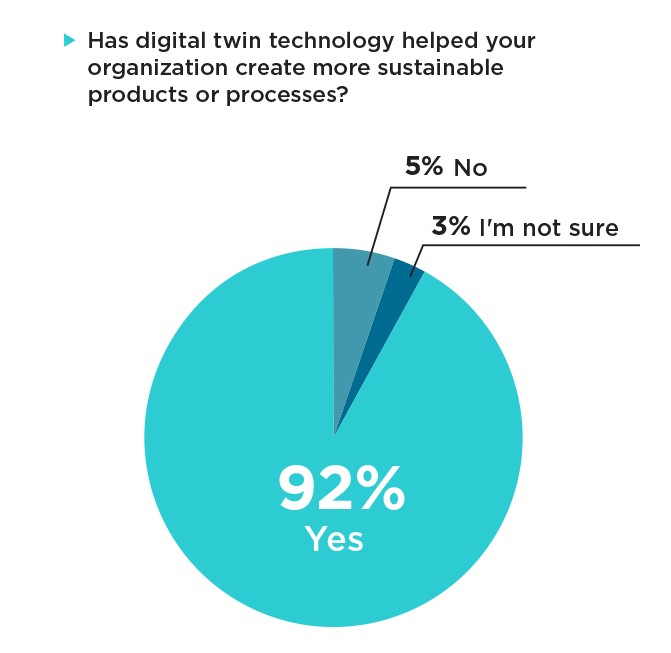
To begin, we see a litany of sustainability-related benefits. 92% of automotive respondents that use digital twin technology said it has helped their organization create more sustainable products and processes. Moreover, respondents from the automotive sector were the most likely to say their organizations are currently using digital twin technology to reach sustainability objectives at 63% – eight points higher than the overall survey average. And 78% of respondents who use digital twin technology named energy savings and/or efficient use of resources as ways the technology helps their organizations meet their sustainability objectives.

The data also suggests that digital twin technology is helping automotive organizations innovate on the product development side. 97% of respondents said the technology better informed the development of new products. Additionally, the automotive industry was the most likely industry to say that digital twin technology made their products and processes easier to refurbish and/or reuse at 51% – 10 points above the overall survey average.
The findings – especially as they concern sustainability – are encouraging at a time when automotive organizations worldwide are looking to become leaders in electric vehicle (EV) technology and slash vehicles’ carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. As the world attempts to mitigate climate change’s worst effects by minimizing CO2 emissions and energy use, EV technology has the power to transform people’s day-to-day lives and help us keep temperature rise below international targets. Altair already showcases innovations that make automotive technology lighter and more sustainable with the annual Altair Enlighten Award, the industry’s only award dedicated to lightweighting and sustainability. It’s clear that digital twin technology will drive many of the innovations that will revolutionize the automotive industry, both today and in the future.
Expectations of Digital Twin Technology’s Future in the Automotive Industry
Lastly, we’ll recap what the data presented on the future of digital twin technology in the automotive industry and where respondents believe the technology will go in the coming years.
To start, 92% of respondents believe their leadership would be more likely to invest in digital twin technology if they better understood its benefits – a figure seven points higher than the overall survey average and the highest figure among any other industry in the survey.
Of respondents who said their organization doesn’t currently leverage digital twin technology, 22% expected their organization to invest within the next six months or less – this was the second-highest proportion of such responses among the other industries surveyed. The automotive industry’s proportion for this question was 11 points higher than the overall survey average. This response data suggests there’s a growing desire to adopt digital twin technology – and do it fast.
Respondents also saw a myriad of potential benefits on the development and quality side as well. Overall, the automotive industry was the most likely industry to say that digital twin technology will improve product quality in the future at 50%, 11 points above the overall survey average. This is another aspect that will be vital in the race for better, more durable EVs.
And in what has proven to be one of the survey’s most fascinating questions regardless of sector, 38% of automotive respondents believed digital twin technology will make physical prototyping obsolete within the next four years or sooner. This is noteworthy coming from an industry that pioneered dynamic physical prototyping and is still synonymous with the process today. What would a world without the crash test dummy look like in the automotive industry? We may soon find out!
Conclusion
The report’s data hints at a future where the automotive industry – which has so long played an outsize role in CO2 emissions – is driven by reliable, sustainable EVs powered by the innovations and real-time insight digital twin technology can provide. Ultimately, the data suggests that the automotive industry is already embracing the technology, even if they haven’t quite maximized its potential. Hopefully, with the transformational power of digital twins in their toolkit, automotive organizations around the world can start developing vehicles that minimize carbon footprint and help the world move toward a carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative mindset.
To read the full report on digital twin in the automotive sector, click here. To read the overall global survey report, click here. To learn all about Altair’s digital twin capabilities, visit https://altair.com/one-total-twin.
Additional Altair Digital Twin Resources
- Infographic: Digital Twins are Driving the EV Revolution
- Infographic: Why Digital Twin Adoption Rates are Skyrocketing
- Infographic: Can Digital Twins Save the Planet?
- Infographic: Bridging the Gaps in Digital Twin Understanding, Adoption, and Usage
- Article: Overview - What is Digital Twin Technology?
- Article: Digital Twin's Sustainability Potential
- Report: 2023 Global Digital Twin Survey Report: Manufacturing




